1. What is fire?
2. What three criteria must be fulfilled in order for
something to burn?
3. What is autoignition temperature?
4. When the fire is on – what is almost always created?
5. Describe the cellular respiration reaction
6. Describe the combustion reaction
7. Describe the photosynthesis reaction
8. Connection between photosynthesis, cellular respiration,
combustion?
9. What three ways are there to extinguish a fire?
10. Flash point
11. Energy level diagram
What is
fire?
Fire is a chemical reaction between a combustible substance
and oxygen. In order for the combustible substance to burn,
the temperature must also reach a certain ignition
temperature. Wood begins to burn at 300 °C and hydrogen at
approx. 510 oC. The reaction energy is radiated
out to the surroundings as visible light and as heat
radiation (heat).
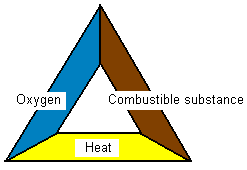
What three criteria must be fulfilled in order for
something to burn?
To make it burn three criteria must be met. There must
be a combustible substance (eg. wood), there must be oxygen
and also a certain temperature must be reached before it
starts to burn. All is summarized in the below “fire
triangle”. If anything is missing in the fire triangle it
will not burn.
What is autoignition temperature?
The autoignition temperature is the temperature the
combustible substance must have to start burning.
When the fire is on – what is almost always
created?
When it burns almost always is created carbon dioxide and
water. At the same time heat radiation is emitted, released
(energy).
Describe the cellular
respiration reaction
The cellular respiration reaction takes place continuously
in our body. We eat e.g. spaghetti containing glucose
molecules as small spirals called starch. The starch is cut
into free glucose molecules by our digestion. These glucose
molecules are absorbed by our small intestinal wall and are
transported through our blood stream to our cells. Here the
glucose is used as energy. At a temperature of only 37 °C
the glucose converts into energy by our cells. In order for
the reaction to happen it requires certain enzymes in the
cells. These enzymes make the reaction occur already at a
temperature as low as 37 oC. The energy is released as heat
and high energy molecules (ATP molecules). Below is the
reaction that occurs in the cells. Note that the waste
products are carbon dioxide, water and energy.
Oxygen + glucose  carbon dioxide + water + energy
carbon dioxide + water + energy
6O2 + C6H12O6  6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
Describe the combustion reaction
The combustion reaction for glucose is exactly the same
reaction as the cellular respiration reaction above. The
difference is that the combustion reaction occurs at higher
temperature. When glucose molecules are joined to form
cellulose building up tree trunks (wood), the temperature
needs to be as high as approximately 300 °C before the
reaction starts, i.e. before it starts to burn.
Oxygen + glucose  carbon dioxide + water + energy
carbon dioxide + water + energy
6O2 + C6H12O6  6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
Describe the
photosynthesis reaction
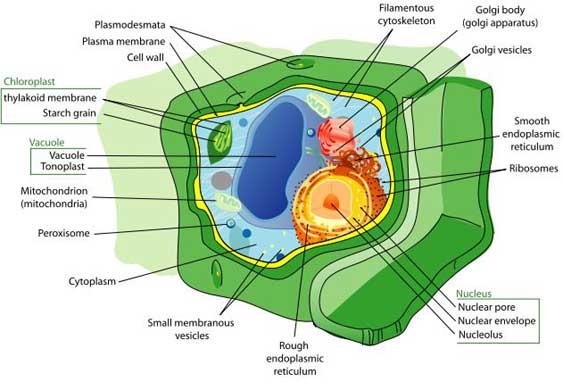
Above is shown a plant cell. A plant cell contains
chloroplasts with chlorophyll.
The green chlorophyll helps the photosynthesis reaction to
occur. (Info about picture)
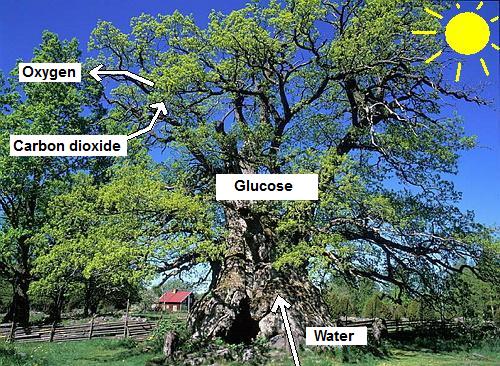
Land plants absorb carbon dioxide gas from the air. Water
plants absorb carbon dioxide gas dissolved in the water.
Instead, land and water plants leave off oxygen. The
chemical reaction describing the process is called the
photosynthesis reaction:
Carbon dioxide + water + energy  glucose + oxygen
glucose + oxygen
6CO2 + 6H2O + energy (sunlight)  6O2 + C6H12O6
6O2 + C6H12O6
Apparently, the plants need carbon dioxide, water and
sunlight (energy) in order to produce oxygen. At the same
time glucose is created. The glucose is used for the
construction of the tree or plant. The glucose is used to
build up leaves, stems but also the fruits.
Trees / plants / shrubs that grow can put together glucose
molecules into starch or cellulose.
A plant can use glucose to form starch (potato, wheat, root
crops). A giant starch molecule has about 300-400 glucose
molecules joined together in a row as a spiral.
Cellulose is made up of glucose molecules joined together in
rows as long fibers. The number of glucose molecules joined
in a row is about 1000-1200 pieces. Cellulose builds for
examples the tree-trunk and other plant parts.
Connection between photosynthesis,
cellular respiration,
combustion?
The cell respiration reaction or the combustion reaction:
Oxygen + glucose  carbon dioxide + water + energy
carbon dioxide + water + energy
6O2 + C6H12O6  6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
Photosynthesis reaction:
Carbon dioxide + water + energy  oxygen + glucose
oxygen + glucose
6CO2 + 6H2O + energy (sunlight)  6O2 + C6H12O6
6O2 + C6H12O6
These two reactions are opposites. We humans (or animals)
cannot live without green plants and green plants cannot
live without animals. Look at the reactions then you'll see
that photosynthesis emits oxygen that humans and animals
need for their respiration. The oxygen is needed for the
cellular respiration reaction.
What three ways are there to
extinguish a fire?
If only one of the three things is taken away from the fire
triangle the fire goes out.

1. Take away the fuel (combustible substance)
2. Take away the heat by cooling the fuel with e.g. water.
3. Oxygen can be removed by excluding oxygen (veiling it).
If for example oil is burning in a pan on the stove, you can
put on the lid. The oxygen under the cover is consumed in
the combustion reaction and then the fire goes out. Other
situations may require so-called fire blanket laid over the
fire veiling off oxygen until the fire "suffocates".
Question: How can we remove the above parts from the fire
triangle to stop the cellular respiration reaction to occur
in our cells?
Flash point
This is the temperature reached when a substance releases
flammable gases. Gasoline emits flammable gases already at
-28 oC. So even when it is winter and -28 °C a lit cigarette
ignites gasoline gas that has accidentally been released
from a gas station.
Energy level diagram
Energy level in the starting substances compared to the
energy level in the substances formed during combustion
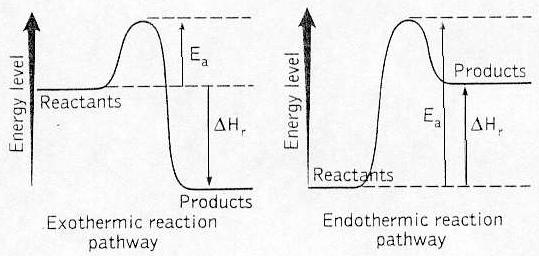
In cases 1 and 2 (both graphs), energy is consumed to make
the reaction occur. This energy EA is called activation
energy. The hill (EA) represents the barrier to overcome for
the reaction to take place. When the hill is passed, the
energy is released. When the energy released is greater than
the activation energy, the reaction is exothermic.
Considering the whole reaction, there is more energy
released than consumed in the reaction. Energy is released.
Examples of such reactions are the cellular respiration
reaction or the combustion reaction. Excess cellular
respiration energy in our body is re-coupled to the reaction
making the body having a temperature of about 37 oC, and for
the creation of ATP-molecules. The reaction can continue.
Excess energy in a combustion reaction is used as activation
energy, and some radiates as heat energy and visible light.
In case 2, the energy that is released is less than the
activation energy for the reaction. Such a reaction is
called an endothermic reaction. Therefore, energy needs all
the time to be supplied to the reaction for it to take
place. An example of such a reaction is the photosynthesis
reaction. The sun supplies energy during the day.
Copywrite NGU, Northern Pontifical Academy 2025 (A.I.C.)