1. How is an atom built and what parts does it contain,
the properties of the parts?
2. What is an isotope; give examples?
3. Mass number, atomic number, and how they are written
together with the chemical symbol?
4. How electrons are distributed in atom shells?
5. Radiation, radiation properties, radioactivity
6. Half-life
7. Carbon 14 method
8. Fission and fusion
9. Questions
How is an
atom built and what parts
does it contain, the properties of the parts?
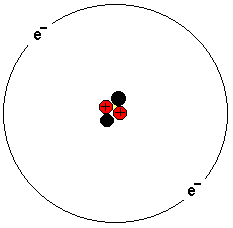
The picture shows a helium atom. It has two protons, two
neutrons and two electrons. The atom consists of a nucleus
and electrons orbiting around.
The atom nucleus consists of protons and neutrons. Protons
are positively charged and neutrons are neutrally charged.
The atomic weight is made up essentially of the atomic
nucleus. The task of the neutrons is to hold together the
protons.
Electrons are negatively charged. In an atom, the number of
electrons is exactly the same as the number of protons in
the nucleus.
If the nucleus is big as a “putter and ball” and located in
the middle of Ullevi Stadium (Sweden), the electrons orbit
outside the stands and are the size of pinheads. Most of the
atom is thus void or vacuum.
An atom is so small that it can only be seen through an
electron microscopy. An electron microscope can magnify
500,000 times.
What is an isotope; give examples?
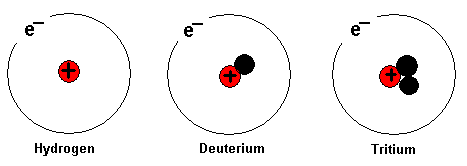
Above is the hydrogen atom. The hydrogen atom has one proton
in its nucleus. The element will be hydrogen, although the
number of neutrons varies in its nucleus. Usually the
hydrogen atom has no neutron at all. When an element can
have different numbers of neutrons in its nucleus it is said
that the different variants are isotopes of the element.
Above are the isotopes of hydrogen, which are hydrogen,
deuterium and tritium. All three atoms above are still the
element hydrogen. Heavy water contains the isotope deuterium
instead of normal hydrogen.
Mass number, atomic number, and how they are written
together with the chemical symbol?
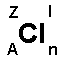
Above is the chemical symbol of chlorine (Cl). Around
is written a number of letters.
A = Atomic number. The atomic number indicates the number of
protons in the nucleus: 1H (hydrogen) and 2He (helium).
Z = Mass number. The mass number shows the number of protons
plus the number of neutrons in the nucleus, eg. 1H
(hydrogen) and 4He (helium).
l = Charge. If the element is in ionic form the charge is
shown here. E.g. Na+ and SO42-.
n = Number of atoms connected. E.g. H2 (hydrogen molecule),
F2 (fluorine molecule).
How electrons are distributed in atom shells?
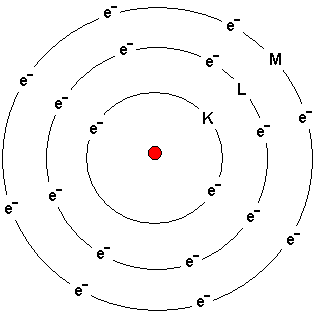
The atom to the left depicts Argon - an inert gas located on
the far right in the table of elements.
Electrons circle in orbits around the nucleus.
The shells are called from the nucleus outwards the K, L, M
and N shells. The names of the shells are shown in the
picture.
The K-shell can contain a maximum of two electrons.
The L-shell can contain a maximum of eight electrons.
The M-shell can initially contain a maximum of eight
electrons.
Electrons are added the different shells from inside and
outward. If the atom has six electrons, then two of them are
placed in the innermost K-shell and four are placed in the
L-shell.
Radiation, radiation properties,
radioactivity
Radiation is produced when an atom decays. Only atoms with
an built-in instability decay spontaneously. Examples of
unstable atoms are 235U, 137Ce and
14C. These are converted
into other elements or isotopes when decaying.
When atoms decay radiation is created. It can be alpha
radiation, beta radiation or gamma radiation.
Alpha radiation consists of a helium nucleus. 4He2+. This
radiation is charged and is easily stopped by a plain paper.
Beta radiation consists of an electron e-. This radiation is
charged and goes through a plain paper. Beta radiation is
stopped by a piece of wood.
Gamma radiation consists of electromagnetic waves. The
radiation is high energy and is stopped by a 20 cm thick
lead plate. The radiation is dangerous because it can
penetrate the body and cause cell changes.
Alpha radiation, beta radiation and gamma radiation are all
called ionizing radiation. Ionizing radiation has enough
energy to knock out electrons from elements thus creating
ions.
Half-life
Radioactive elements decay. The time it takes for half of a
particular radioactive substance to decay is called
half-life. The time is different depending on the
radioactive substance.
The half-life of 235U is 710 million years, for
137Ce it is
30 years and for 14C it is 5700 years. The half-life of
different radioactive atoms can vary from a fraction of a
second to billions of years.
After a half-life half of the substance remains. After yet
another half-life a quarter of the substance remains, and
after yet another half-life an eight of the substance
remains.
Carbon 14 method
Radioactive substances can be used to determine the age of
different materials. To determine the age of a mountain, the
235U can be used, which decays into 207Pb. For age
determination of organic materials the 14C isotope can be
used. Organic materials all contain carbon.
14C is created in the atmosphere. It is created when the
atmospheric nitrogen is hit by the solar wind giving it more
neutrons. This makes the nitrogen mass number increase and
the result is 14C. When a tree grows, the level of
14C is
constant in the tree material. Also 12C is incorporated into
the tree material. When the tree dies the 14C starts
decaying and the relationship between 14C and
12C changes.
The smaller the amount of 14C in the tree material, the
older the piece of wood.
Fission and fusion
Fission: When splitting atoms we talk about fission. When
atoms are split large amounts of energy is produced. In a
nuclear power plant uranium isotopes are split. Shooting
neutrons against the fuel rods containing at least 3% 235U
starts the entire process. 235U decays into other
radioactive substances. Neutrons also release from the split
uranium isotopes. The released neutrons impact other uranium
isotopes, which are also split. The process continues by
itself and one controls the decay rate by using control
rods. A control rod contains a substance that stops
neutrons. The substance can be cadmium or boron. The entire
reactor core is bathed in water. The water in this case is
also a moderator. The task of the moderator is to slow the
speed of the released neutrons. The reactor core heats up
and the water warms up. The warm water that is often kept
under pressure can have a temperature of about 300 degrees
Celsius. This water warms an external water system where the
water starts boiling. The steam produced makes a turbine
rotate, which means that a generator is spinning. The
generator generates electricity.
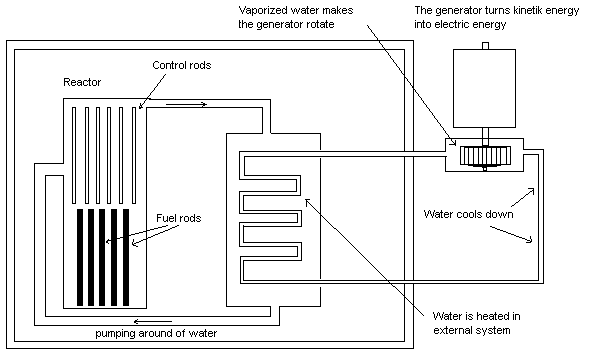
The image shows a nuclear reactor
Fusion: Fusion means that two atoms merge into a heavier
atom. In the sun two hydrogen isotopes merge together.
Deuterium merges with tritium thus forming helium.
Meanwhile, a large amount of heat energy is formed that
makes the sun’s interior maintain a temperature of several
million degrees Celsius. From the center of the sun to the
solar surface the temperature decreases. The sun's surface
has a temperature of 6000 degrees Celsius. The heat from the
sun’s interior makes the sun expand but gravity keeps the
sun together. Those two forces are in balance.
Questions
1. Give the atomic constituents and give their properties?
2. If there are 10 protons in the atomic nucleus, how many
electrons are there in the shells around?
3. Which element has 10 protons in its nucleus?
4. How are electrons distributed on the different shells?
5. What is an isotope?
6. Sometimes there is talk about tritium and deuterium -
which element do they talk about?
7. Sometimes Uranium-235 is mentioned. 235 is the mass
number. How is the number 235 written along with U (the
chemical symbol of uranium)?
8. Why is Cesium-137 dangerous?
9. What is alpha radiation? How can it be stopped?
10. What is beta radiation? How can it be stopped?
11. What are gamma rays? How can they be stopped?
12. How much remains of Cesium-137 after 30 years, 60 years
and after 90 years?
13. How do you determine the age of organic materials?
14. How many electrons can there be at the maximum in the
K-shell and the L-shell?
15. What is nuclear fission and how does it work?
16. How does a nuclear power plant work – explain?
17. What is a moderator?
18. What is fusion? Where does it happen?
Copywrite NGU, Northern Pontifical Academy 2025 (A.I.C.)